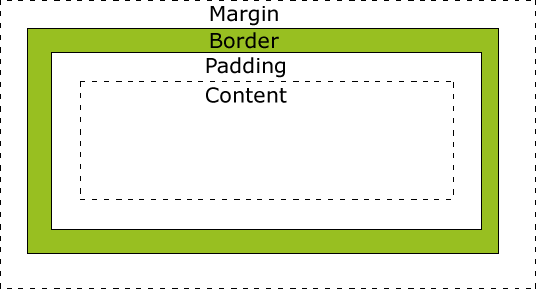
What is CSS?
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a stylesheet language used to describe the presentation of a document written in HTML or XML. CSS describes how elements should be rendered on screen, on paper, in speech, or on other media.
Note: CSS is not a programming language; it's a style sheet language that defines how HTML elements are displayed.